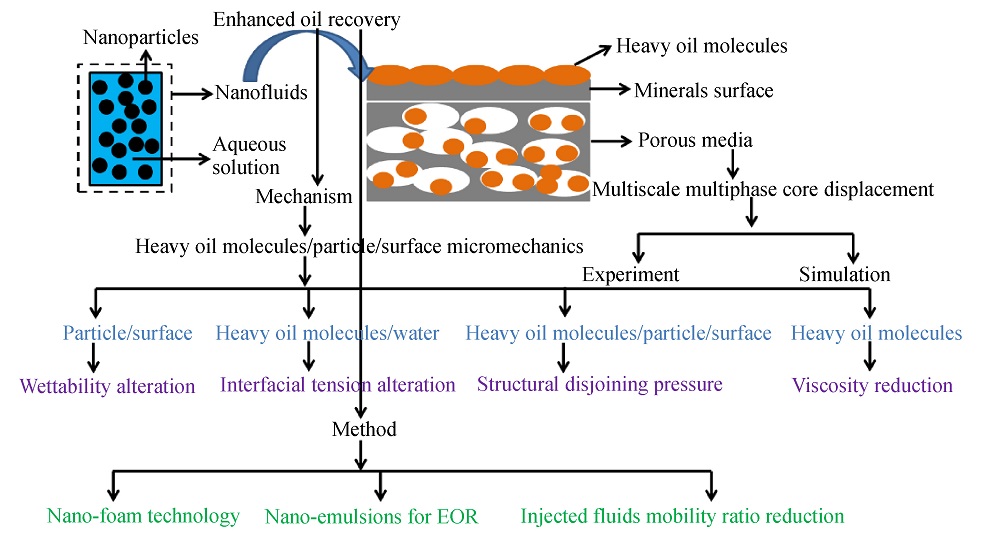
1 Introduction
2 Heavy oil molecules/particle/surface micromechanics
2.1 Particle/surface micromechanics: wettability alteration
2.1.1 Concepts of nanofluids that affect wettability
2.1.2 Analysis of factors that influence wettability
Tab.1 Contact angle alteration and oil recovery with different nanoparticles, minerals, aqueous phases, and temperatures |
| Ref. | Nanoparticle | Mineral type | Aqueous phase | Temperature | Oil recovery increase | Contact angle alteration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [135] | Fluorinated nano SiO2 | Limestone | Deionised water | 80 °C | – | – |
| [136] | Al2O3 | Sandstone | PRNS | Ambient temperature | – | 142° to 0° |
| [137] | SiO2 | Sandstone | Brine | 20 °C | 36.49% | 54° to 22° |
| [138] | TiO2 | Sandstone | Brine | Ambient temperature | – | 125° to 90° |
| [139] | SiO2 | Quartz plane | Brine | Ambient temperature | – | 39° to 26° |
| [64] | Al2O3 | Sandstone | Synthetic brine | Ambient temperature | 20.2% | Higher than 82° |
| Fe2O3 | 17.3% | 134° to 100° | ||||
| SiO2 | 22.5% | 134° to 82° | ||||
| [81] | Al2O3 | Limestone | Deionised water | 26 °C, 40 °C, 50 °C, 60 °C | 9.9% | 82° to 61° |
| TiO2 | 6.6% | 82° to 46° | ||||
| SiO2 | 2.9% | 82° to 18° | ||||
| [140] | γ-Al2O3 | Calcite | Deionised water | Ambient temperature | 11.25% | 119° to 38° (0.5%) |
| [141] | TiO2 | Carbonate | Deionised water | Ambient temperature | – | 144° (water), 95° (oil) |
| SiO2 | 139° (water), 88° (oil) | |||||
| CNT | 140° (water), 85° (oil) | |||||
| [80] | Al2O3/TiO2/SiO2 | Sandstone | 3 wt-% NaCl, PVP | Ambient temperature | 6% | 56.09° to 21.64° |
| [142] | SiO2 | Calcite | 0.05 mol·L–1 NaCl | Ambient temperature | – | 156° to 41.7° |
| [172] | SiO2 | Carbonate | Brine | Ambient temperature | – | 122° to 18° |
| [144] | SiO2 | Glass | Ethylene glycol | Brine, SDS | 18.1% | 88° to 25° |
| [145] | SiO2 | Sandstone | PAM, SDS | 30 °C, 90 °C | 24.7% | – |
| [82] | ZrO2, NiO | Limestone | C16TAB, TX-100 | Ambient temperature | – | 152° to 35° |
| [146] | FSPNs/SiO2 | Plate | Ethanol | Ambient temperature | 28% | 134.4° to 23.7° |
| [173] | SiO2 | Quartz | Brine | Ambient temperature | 4.48% to 10.33% | – |
| [133] | SiO2 | Calcite | Brine | 23 °C to 60 °C | – | 145° to 56° |
| [147] | Al2O3(ZrO2) | Carbonate | TX-100 | Ambient temperature | – | 85° to 62° (71°) |
| SDS | 92° to 75° (84°) | |||||
| CTAB | 70° to 52° (60°) | |||||
| [149] | SiO2 | Sandstone | Brine, Tween® 20 | Ambient temperature | – | 121.7° to 39.7° |
| [150] | SiO2 | Carbonate | Brine | Ambient temperature | – | 138.7° to 50.8° |
| [151] | SiO2 | Glass substrate | Brine | 60 °C | 25% | 142° to 35° |
| [152] | Fe3O4/chitosan | Sandstone | Brine | Ambient temperature | 10.8% | 127° to 92° |
| [153] | SiO2 particles | Berea core slice | Xanthan gum | Ambient temperature | 20.82% | 86.2° to 50.4° |
| [154] | ZnO | Calcite | SDS | Ambient temperature | 11% | 11.82° |
| [65] | SiNP-NH2 | Sandstone | Soloterra 964, brine | 65 °C | 17.23% | 130.2° to 43.4° |
| [155] | CaCO3 | Calcite | Surfactant | 25 °C to 80 °C | – | 106° to 50° |
| [156] | SiO2 | Sandstone | HPAM, brine | Ambient temperature | 6.7% | 55.7° to 31° |
| Al2O3 | 11.3% | 55.7° to 25.1° | ||||
| [159] | ZnO/SiO2/xanthan gum | Carbonate | LSW | Ambient temperature | 19.28% | 137° to 34° |
| [83] | SiO2 | Glass | Deionised water | Ambient temperature | 9% | 135° to 88° |
| [160] | Hydrophilic SiO2 | Limestone/dolomite | SDS, brine | Ambient temperature | 15% | 165.65° to 65.75° |
| [161] | SiO2 | Carbonate | Saline | 80 °C | 8% to 17% | 141° to 23° |
| [166] | MnZn ferrite | Glass plate | Brine, SDBS | Ambient temperature | – | 48.64° to 11.97° |
| [167] | SiO2 | Berea sandstone | Brine, rhamnolipid | Ambient temperature | 5.3% to 6.8% | 145° to 54° |
| [162] | SiO2 | Calcite | NaCl | Ambient temperature | 18% | 140° to 38° |
| [157] | Al2O3 | Sandstone | HPAM | 27 °C, 60 °C, 90 °C | 10.6% | 100.3° to 60.6° |
| SiO2 | 6.11% | 100.3° to 78.6° | ||||
| [158] | CuO/TiO2/PAM | Carbonate | Deionised water | Ambient temperature | – | 151° to 14.7° |
| Sandstone | 135.25° to 11.75° | |||||
| [168] | NiO/SiO2 | Carbonate rocks | Deionised water/polyethylene glycol | Ambient temperature | – | 176° to 40° |
| [148] | Al2O3 | Rock samples | TX-100/SDBS | Ambient temperature | – | 16.0° (TX-100), 25° (SDBS) |
| CuO | 13.7° (TX-100), 22.3° (SDBS) | |||||
| TiO2 | 12.5° (TX-100), 25.9° (SDBS) | |||||
| CN | 7° (TX-100), 20.5° (SDBS) | |||||
| SiO2 | 16.9° (TX-100), 25.8° (SDBS) | |||||
| [169] | TiO2/quartz | Carbonate pellets | Seawater | 30 °C, 50 °C, 70 °C | 21% | 103° to 48° |
| [170] | Fe3O4@SiO2@xanthan | Carbonate rock | Deionised water | Ambient temperature | – | 134° to 28° |
| [171] | Fe3O4 | Carbonate rock | Polyvinyl alcohol, hydroxyapatite | Ambient temperature | – | 116° to 62° |
| [164] | SiO2 | Glass surface | Brine water | Ambient temperature | 75% (brine) | 120° to 0° (oil-wet) |
| [165] | SiO2 | Sandstone rock | Brine water | 70 °C | 18.46% (LNS) | 180° to 65° |
| [163] | SiO2 | Carbonate rock | Brine water | 70 °C | 2.8% (LNS) | 180° to 120° |
2.1.3 Effect of nanoparticle species on wettability alteration
2.1.4 Influence of salinity on wettability alteration
2.1.5 Effect of temperature on wettability alteration
2.1.6 Wettability alteration for different minerals
2.1.7 Effect of the mixture of polymers/surfactants and nanoparticles on wettability
2.1.8 Micro-mechanism of wettability alteration

Fig.11 Total interaction energy per unit area versus water film thickness for the rock surface-aqueous phase-oil systems when AH (oil) = 4.5 × 10–20 J. The aqueous phases are tap water (TW) and TW+ nanoparticle with different carbon nanopartiles. Reprinted with permission from ref. [182], copyright 2021, Elsevier. |
2.2 Heavy oil molecule/water micromechanics: interfacial tension alteration
Tab.2 Variation in oil/water interfacial tension caused by different concentrations of nanofluids, oil phase, and temperature |
| Ref. | Nanofluids type | Dispersion phase | Nanofluids concentration | Oil phase | Temperature | Interfacial tension without nanoparticle/(mN·m–1) | Interfacial tension with nanoparticles/(mN·m–1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [185] | Hydrophilic SiO2 | Alkylpoly-oxyethylene | – | Medium | – | 31 | 1.7 |
| [186] | PSS-SiO2 | – | 1–5 mg·L–1 | Trichloroethylene | Ambient temperature | 22.5 | 14.5 |
| [187] | SiO2 Aerosil 200 | CTAB | 0.01–5 | Paraffin oil | 25 °C | 52 | 5 |
| [188] | Colloidal SiO2 | SDS, TX-100, CnE4 | – | Trichloroethylene | 22.5 °C+ 0.5 °C | 40 | 2 |
| [189] | TiO2 | Deionised water | 0.1 wt-% | Mineral oil | 25 °C–55 °C | 52 | 36 |
| [190] | Colloidal SiO2 | CTAB | 1 wt-% | Hexane | 20 °C | 72.5 | 21 |
| [191] | Bi2Te3 | Deionised water | 0.318 wt-% | Gas-liquid | – | 72 | 48 |
| [192] | Gold | Deionised water | 0.0218 wt-% | Gas-liquid | – | 72.38 ± 0.41 | 67.53 ± 0.66 |
| [193] | Nonferrous metal | Sulfanole | 0.001 wt-% | 7 cp | 25 °C | 10.9 | 1.09 |
| [194] | Laponite/silver/ Fe2O3 | 1% PVP | 2 wt-% | – | – | 73.6 | 40.97 |
| [195] | SiO2 | Lecithin/tween 60 | 1% | Vegetable oil | 25 °C | 11 | 6 |
| [196] | SiO2 | 5 wt-% NaCl | 3 g·L–1 | Light oil | Ambient temperature | 26.5 | 1.95 |
| Heavy oil | 28.3 | 7.3 | |||||
| [197] | SiO2 | Ethanol | 0.4 | – | Ambient temperature | 26.3 | 1.7 |
| [198] | Hydrophilic Al2O3 | Saturated base fluid | 1–10–5 to 5–10–4 | Toluene | 293.2 K–323.2 K | 37.1 | 55.7 |
| Hydrophobic Al2O3 | 14.4 | ||||||
| [199] | Hydrophilic SiO2 | 500 ppm SDS | 1000 ppm | Kerosene | Ambient temperature | 7.43 | 6.10 |
| 6000 ppm SDS | 2.85 | 4.24 | |||||
| hydrophobic SiO2 | 500 ppm SDS | 7.43 | 3.71 | ||||
| 6000 ppm SDS | 2.85 | 4.64 | |||||
| [200] | SiO2 | Brine | 10% | Crude oil | 25 °C ± 1 °C | 16 ± 2 | 1.4 ± 0.3 |
| [201] | ZrO2 | Deionised water | 1 g·L–1 | n-Heptane | 23 °C ± 0.5 °C | 51.4 | 36.8 |
| [202] | Magnetite | SDS | 0–5×10–4 | n-Hexane | 288.2 K–308.2 K | 51.4 | 41.5 |
| [64] | Fe2O3 | Synthetic brine, propanol | 0.3 | Degassed reservoir oil | 25 °C | 38.5 | 2.25 |
| Al2O3 | 2.75 | ||||||
| SiO2 | 1.45 | ||||||
| [203] | SiO2 | 0.5 wt-% SDS | 0–2 wt-% brine | Crude oil | 60 °C | 21.7 | 4.2/6.3 |
| [139] | SiO2 | Brine | 0.05 | Degassed light crude oil | 22 °C | 19.2 | 16.9 |
| 35 °C | 12.57 | 15.60 | |||||
| 50 °C | 12.14 | 12.80 | |||||
| [80] | Al2O3 | 3 wt-% NaCl, 1 wt-% PVP | 0.05 | Degassed crude oil | – | 19.2 | 12.8 |
| SiO2 | 17.5 | ||||||
| [204] | SiO2 | Deionised water | 0.1 | Oil | Ambient temperature | 13.62 | 10.69 |
| [205] | ZrO2 | 2000 ppm SDS | 100 ppm | Heavy crude oil | 25 °C | 16 | 3.1 |
| 3000 ppm C12TAB | 18.4 | 5.4 | |||||
| [206] | SiO2 | 5% NaCl | 0–6 g·L–1 | Crude oil | Ambient temperature | 26.5 | 38.4 |
| [207] | SiO2 | SDS | 1 × 10–4 | n-Hexane | 293.2 K | 48.9 | 31.2 |
| [208] | SiO2/TiO2/ZnO | Tween 20 | 0.1 wt-% | Four oils | 25 °C | – | – |
| [145] | Hydrophilic SiO2 | PAM | 0.5–2 wt-% | Crude oil | 30 °C–90 °C | 18.03 | 10.22 |
| SDS-PAM | 4.9 | 1.12 | |||||
| [144] | SiO2 | Brine | Polyethylene glycol 8000 | Oil | Ambient temperature | 43 | 8.8 |
| [209] | SiO2 | CTAB | 0.5–2.0 wt-% | n-Heptane | 25 °C | 39 | 41 |
| [210] | SiO2 | 2-Poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) | 0.1–0.2 | n-Decane | Ambient temperature | 47 | 35 |
| [211] | SiO2 | Oly2(DMAEMA) | 0.1 | Bitumen oil | Ambient temperature | 27 | 14 |
| [154] | ZnO | SDS | 0.05–0.5 | – | – | 34.52 | 30.74 |
| [212] | SiO2 | CTAB | – | Kerosene | 298.2 K | 48.7 | 7.5 |
| [152] | Fe3O4 | Seawater | 0.01–0.03 wt-% | Crude oil | 25 °C | 30 | 17.29 |
| 40 °C | 26.32 | 14.80 | |||||
| 60 °C | 22.49 | 14.47 | |||||
| [96] | PK-Fe3O4 | Deionised water | 0.2 wt-% | Bitumen (10%) | Ambient temperature | 14.40 | 8.59 |
| [153] | SiO2 | Xanthan gum | 0.1–0.5 | Crude oil | 30 °C | 17.8 | 8.54 (0.5 wt-%) |
| 70 °C | 14.64 | 6.46 (0.3 wt-%) | |||||
| [213] | CuO | Deionised water | 0–8 wt-% | – | 25 °C | 72 | 38 |
| [168] | NiO/SiO2 | Deionised water | 12‒30 wt-% | Soroush oil | – | 29.02 | 1.28/<1 |
| [157] | SiO2/Al2O3 | Brine | – | Heavy mineral oil | 27 °C | 27.5 | 9.3/11.5 |
| [214] | Al2O3/ZrO2/SiO2/CN | CTAB/SDBS/TX-100/SDS | 0.1–2 wt-% | n-Decane | 303 K/323 K/353 K | 47.53 | 2.98 |
| [103] | SiO2-C12 JNPs | Brine | 0.05 wt-% | Crude oil | 50 °C | 28 | 2.28 |
| [92] | Hydrophilic SiO2 | SOS/EHAC, brine | – | n-Decane | 25 °C to 65 °C | 11.8 | 7.8 |
| [165] | SiO2 | Brine (LSW) | – | Crude oil | 70 °C | 6.20 | 2.31 |
| [163] | SiO2 | Brine (LSW) | 0.05 wt-% | Crude oil | 70 °C | 6.20 | 2.31 |
2.2.1 Role of nanofluids in oil/water interfacial tension

Fig.13 Interfacial tension of different oil/water systems: (a) n-hexane, (b) n-decane, (c) n-heptane, and (d) toluene, in the absence of nanoparticles and in the presence of 0.1 wt-% of ZnO, TiO2, and SiO2 nanoparticles. Standard deviations are less than 1%. Reprinted with permission from ref. [208], copyright 2016, the Royal Society of Chemistry. |

Fig.14 Influence of temperature (303 K, 323 K, and 353 K) on the adsorption of (a) Al2O3-surfactant mixtures, (b) ZrO2-surfactant mixtures, (c) SiO2-surfactant mixtures, and (d) CNT-surfactant mixtures at decane/water interface. Reprinted with permission from ref. [214], copyright 2019, Royal Society of Chemistry. |

Fig.15 Variation in interfacial tension versus temperatures: ■, only nanoparticles with a mass fraction of 1.00 × 10–4; ▲, only SDS with a concentration of 0.80 × 10–4 mol·dm–3; ●, mixture of nanoparticles with a mass fraction of 1.00 × 10–4 and SDS with a concentration of 0.80 × 10–4 mol·dm–3. Reprinted with permission from ref. [202], copyright 2014, Royal Society of Chemistry. |
2.2.2 Synergistic effect of nanofluids and surfactants on interfacial tension

Fig.17 (a) Equilibrium interfacial tension of Tween 20 surfactants in presence of 0.1 wt-% of different nanoparticles, i.e., SiO2, TiO2, and ZnO at n-hexane/water interface; (b) interfacial tension data at the concentration range of 0.001–0.05 mmol·L–1 (standard deviations are less than 1%). Reprinted with permission from ref. [208], copyright 2016, Royal Society of Chemistry. |